what was the social impact of the decision in brown v. board of education?
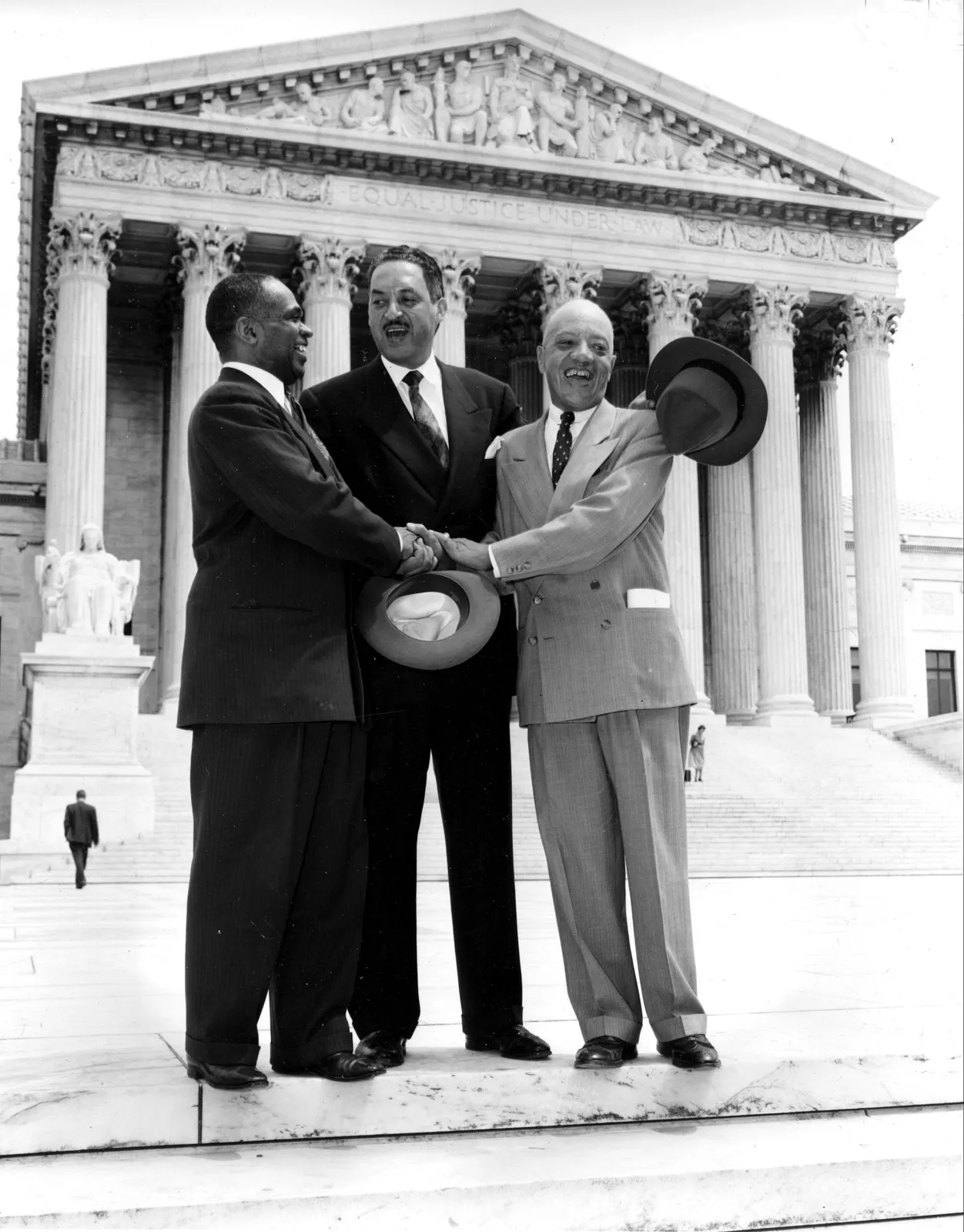
The Supreme Court’s famous ruling in Brown v. Board of Education in 1954 had a significant and lasting effect on American culture. Racial segregation in public schools was ruled to be unlawful by a unanimous court in the case, which contested the validity of the practice. This ruling had a profound impact on American society and education, paving the way for the Civil Rights Movement and inspiring the struggle for equality in several other spheres of public life.
The theory of “separate but equal,” which was established by the 1896 decision Plessy v. Ferguson, provided legal justification for racial segregation in public places, including schools, prior to Brown v. Board of Education. But this precedent was reversed by the Brown decision, which found that “separate educational facilities are inherently unequal.” The decision sent a strong statement that segregation was not only immoral but also a breach of the Constitution’s guarantee of equal protection under the law, directly challenging the widespread racial prejudice of the era. The decades-old institutional architecture of segregation was partially overthrown by this ruling.
The Brown ruling had an instantaneous and profound social impact. It greatly aided the Civil Rights Movement by giving leaders and activists who were working to eradicate racial discrimination legal support for their actions. The ruling sparked campaigns to end segregation in other spheres of American society, including housing, voting rights, and public transit. In addition to inspiring a new generation of activists, such as Rosa Parks, Martin Luther King Jr., and others who would later spearhead demonstrations and campaigns for racial equality, it pushed African Americans to demand their rights.
However, there was strong opposition to the Brown decision’s implementation, particularly in Southern states. The Court’s decision was disregarded by numerous white groups and political figures, which resulted in what became known as “massive resistance.” While some governments closed public schools completely to prevent integration, others adopted “freedom of choice” systems that covertly preserved segregation. Decades of social and legal battles resulted from the opposition, including the civil rights demonstrations and court cases in the 1960s that eventually compelled the federal government to step up its enforcement of desegregation laws.
Notwithstanding the difficulties in putting it into practice, Brown v. Board of Education served as a springboard for additional judicial and legislative developments in the struggle for racial equality. The decision set the stage for other laws that further ended segregation and safeguarded African Americans’ civil rights, such as the Voting Rights Act of 1965 and the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Additionally, the ruling contributed to the gradual dismantling of institutional racism in American society by changing popular perceptions of equality and race.
In conclusion, it is impossible to overestimate the social significance of Brown v. Board of Education. The ruling challenged the practice of racial segregation and upheld the values of equality and justice, marking a watershed in American history. The decision was an important initial step in the greater drive toward racial equality and social justice, even though it did not instantly end discrimination or segregation. The significance of the struggle for social reform and equal opportunity is highlighted by Brown’s legacy, which is still felt in current debates over civil rights, education, and race in America.